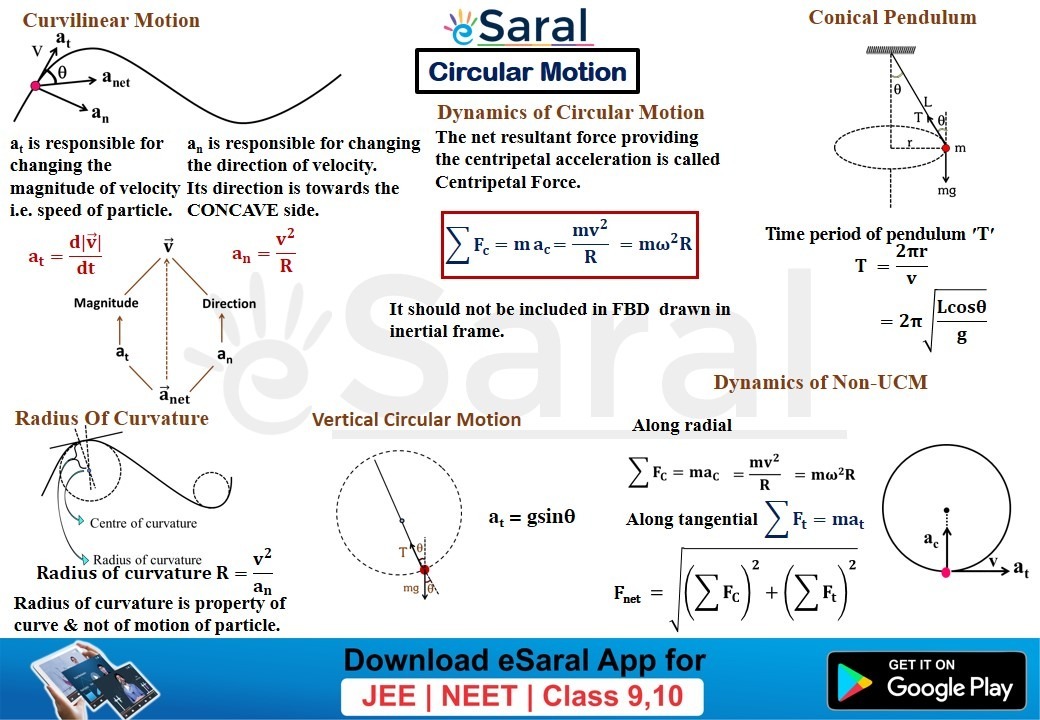
Mind Maps for Circular Motion Revision Class XI eSaral
3.6.1.1 Circular motion Motion in a circular path at constant speed implies there is an acceleration and requires a centripetal force. Magnitude of angular speed, ω = v r = 2πf Radian measure of angle. Direction of angular velocity will not be considered. Centripetal acceleration, a = v2 r = ω2r
Circular motion
Figure 4.5.1: (a) A particle is moving in a circle at a constant speed, with position and velocity vectors at times t and t + Δt. (b) Velocity vectors forming a triangle. The two triangles in the figure are similar. The vector Δ→v points toward the center of the circle in the limit Δt → 0.

2 Uniform Circular Motion Notes PDF Acceleration Velocity
In physics, circular motion is a movement of an object along the circumference of a circle or rotation along a circular arc. It can be uniform, with a constant rate of rotation and constant tangential speed, or non-uniform with a changing rate of rotation.
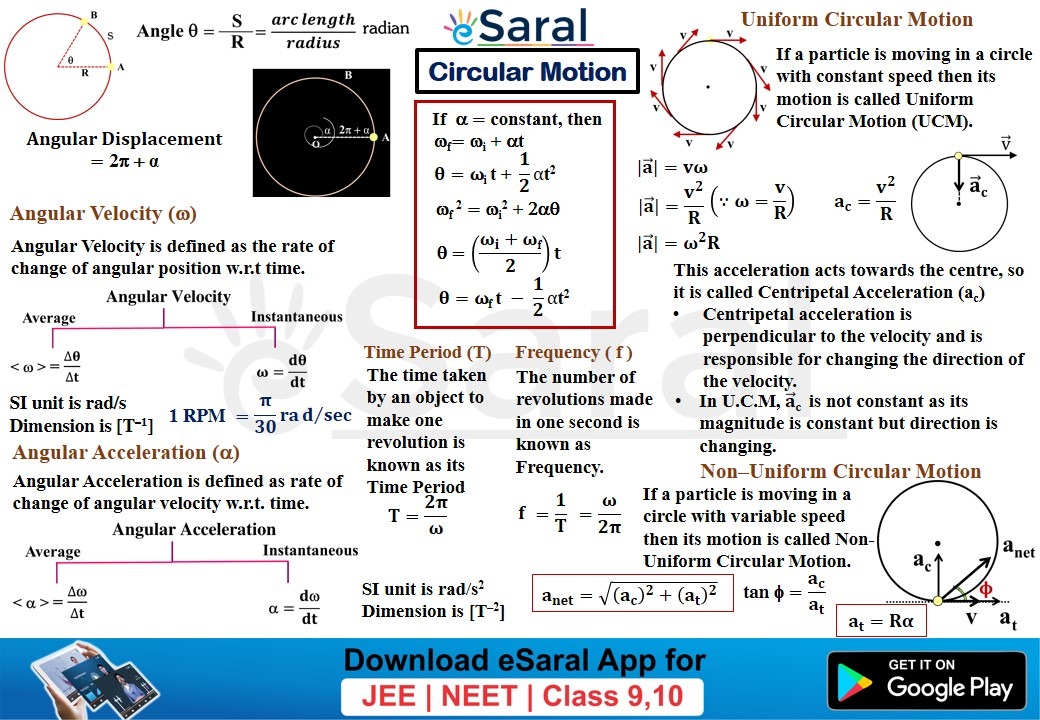
Mind Maps for Circular Motion Revision Class XI eSaral
The simplest case of circular motion is uniform circular motion, where an object travels a circular path at a constant speed. Note that, unlike speed, the linear velocity of an object in circular motion is constantly changing because it is always changing direction.
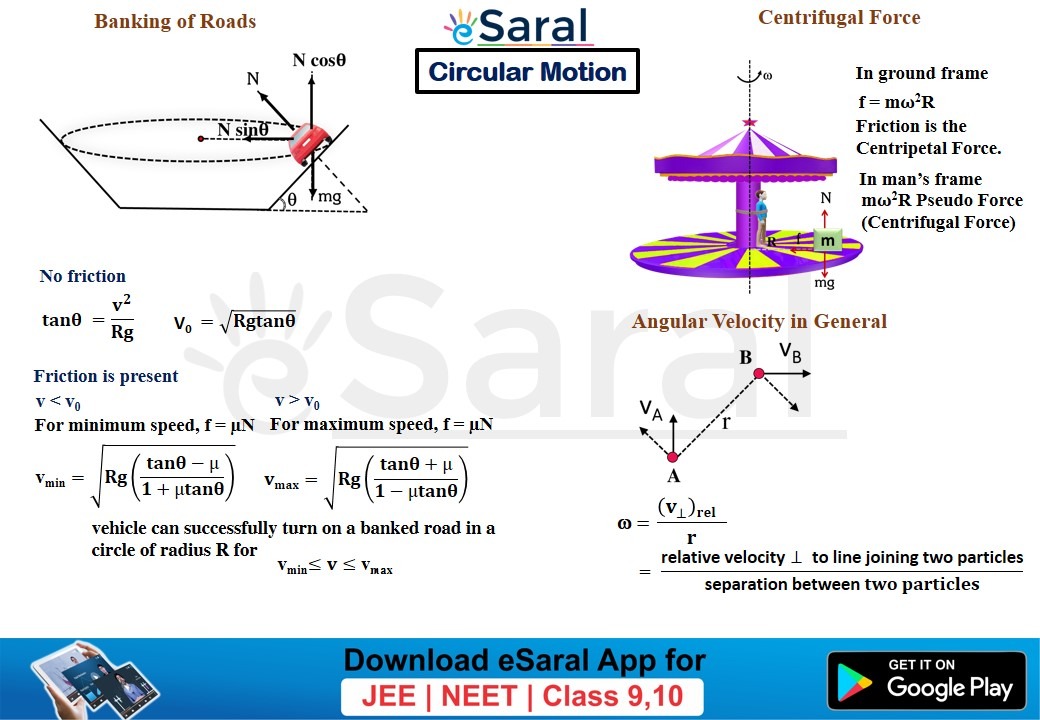
Mind Maps for Circular Motion Revision Class XI eSaral
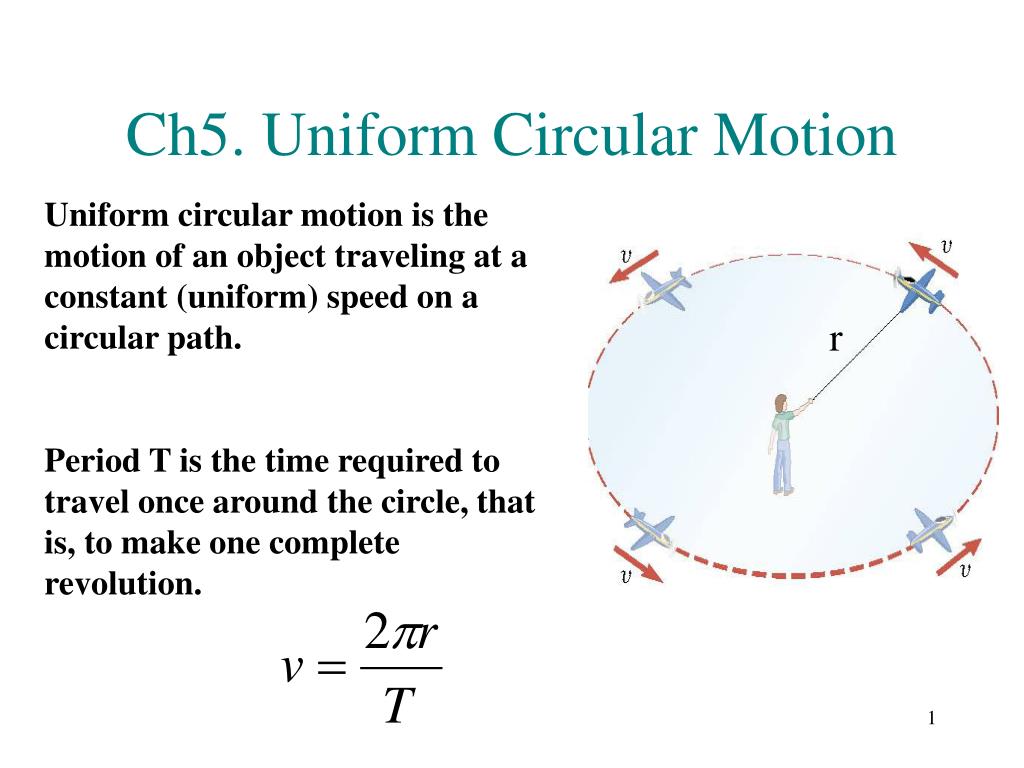
Circular Motion is the motion of an object in a circular path, such as the cornering of a car. The period, T, is the amount of time the object takes to complete one revolution around the circle. The linear velocity depends on distance/time. This is for the velocity along the circumference of the path, or the linear speed.

SOLUTION Uniform circular motion notes Studypool
The motion of the moon around the earth is nearly circular. The motions of the planets around the sun are nearly circular. Our sun moves in nearly a circular orbit about the center of our galaxy, 50,000 light years from a massive black hole at the center of the galaxy.
Circular Motion Notes Class 11th IIT JEE
Uniform circular motion introduction © 2024 Khan Academy Uniform circular motion and centripetal acceleration review Google Classroom Review the key concepts, equations, and skills for uniform circular motion, including centripetal acceleration and the difference between linear and angular velocity. Key terms Equations

Circular Motion Revision Note for JEE Mains & NEET Entrance Exam
Δ v = v r Δ r. Figure 4.18 (a) A particle is moving in a circle at a constant speed, with position and velocity vectors at times t t and t + Δt. t + Δ t. (b) Velocity vectors forming a triangle. The two triangles in the figure are similar. The vector Δv Δ v → points toward the center of the circle in the limit Δt → 0.
Circular Motion Notes Class 11th IIT JEE
Movement of an object while rotating along a circular path is known as circular motion. Circular motion can be either uniform or non-uniform. In this article, let us discuss in brief the uniform circular motion along with examples. Table of Contents: What Is Uniform Circular Motion? Uniform Circular Motion Examples Frequently Asked Questions - FAQs

Circular Motion
Circular motion is described as a movement of an object while rotating along a circular path. Circular motion can be either uniform or non-uniform. During uniform circular motion, the angular rate of rotation and speed will be constant, while during non-uniform motion the rate of rotation keeps changing.

CIRCULAR MOTION revision notes and calculations ALevel Science
In circular motion, an object rotates in a circle around the rotational axis. To find the rotational axis, use the right-hand rule: use the fingers of your right hand to follow the direction of rotation, and your thumb will point along the axis.. Note: this formula is for a particle of mass m at distance r from the axis of rotation. To.

UNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION Notes.pdf Acceleration Velocity
A circular motion is defined as a body movement that follows a circular route. Uniform Circular Motion is the motion of a body traveling at a constant speed along a circular path. The speed remains constant, but the velocity varies. If a particle is traveling in a circle, it must be experiencing some acceleration towards the center, causing it.

Circular Motion Summary YouTube
Circular Motion Velocity and acceleration are both vector quantities An object in uniform circular motion has a constant linear speed However, it is continuously changing direction. Since velocity is the speed in a given direction, it, therefore, has a constantly changing velocity The object therefore must be accelerating
PPT Notes 6.2 Circular Motion PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Circular Motion Definition Circular motion is the movement of an object in a circular path. We are giving a detailed and clear sheet on all Physics Notes that are very useful to understand the Basic. If the magnitude of the velocity of the body in circular motion is not constant, then it is called non-uniform circular motion. Note: Spinning.

NEET Circular Motion All Formulae & Short Notes (Handwritten) AFS
For PDF Notes and best Assignments visit http://physicswallahalakhpandey.com/Live Classes, Video Lectures, Test Series, Lecturewise notes, topicwise DPP, dyn.
BIOLOGY & GEOLOGYAna Trinidad IES AlQazeres UCM Uniform
The motion of a body is said to be circular if the body is always at a fixed distance from a fixed point. The fixed distance is called radius and the fixed point is called the centre of the circular path. Angular displacement: