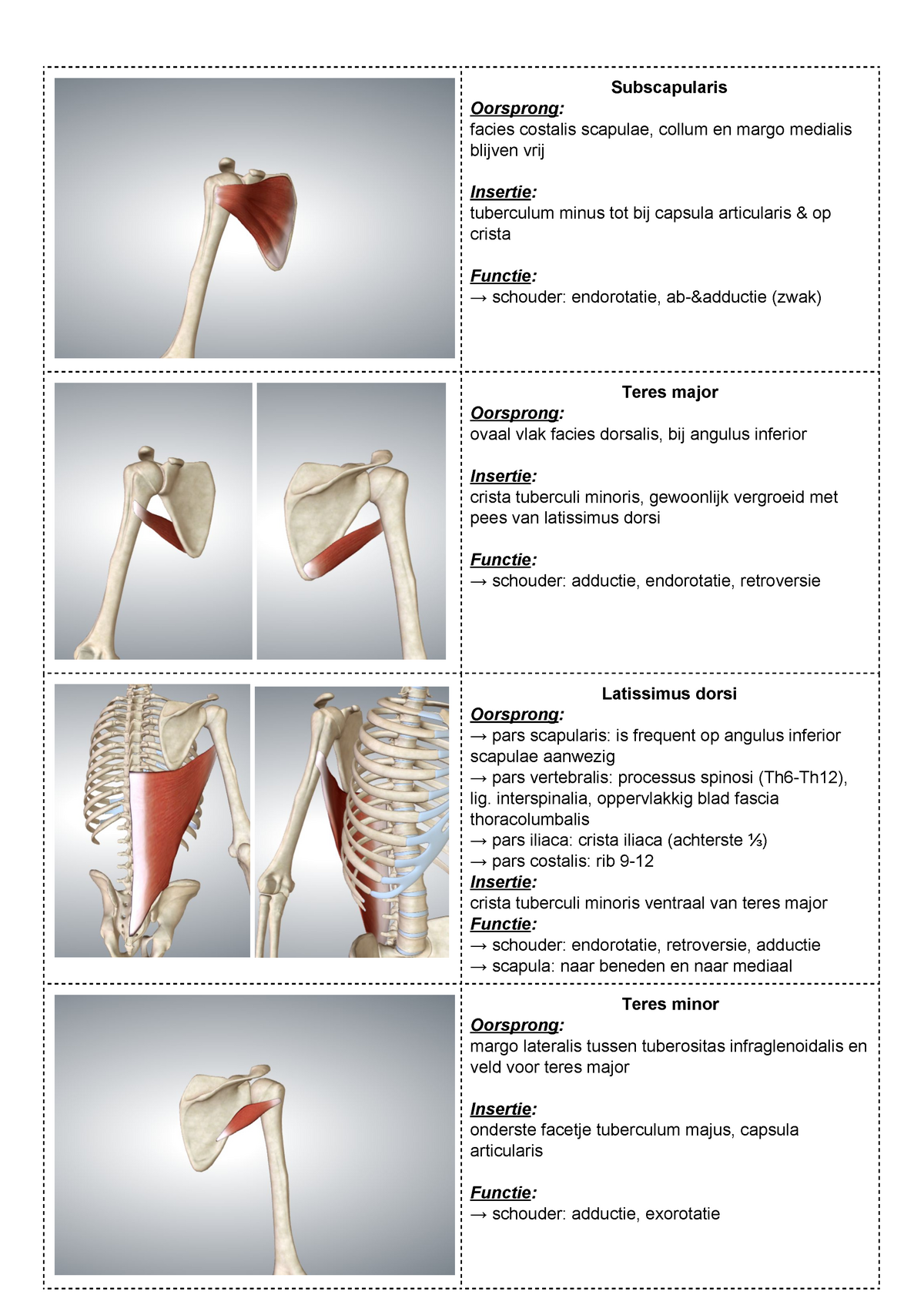
Spieren Subscapularis Oorsprong facies costalis scapulae, collum en margo medialis blijven
A margo medialis scapulae a lapocka (scapula) belső széle és a három közül a leghosszabb. Az angulus superior scapulae és az angulus inferior scapulae között található. Alakja ívelt, középen a legvastagabb és a felső vége tompa. Ennek a szélnek két pereme van: az anterior és a posterior perem. Az anterior részen musculus serratus anterior tapad.

Shoulder blade Dornheim Anatomy
from the margo medialis of the scapula. We wish to communicate our tech-nique of a longitudinal osteotomy of the margo medialis for improved refixa-tion of the muscles. Patients and Methods: 5 patients with subscapular and one patient with a subrhomboid benign tumor were operated using this on technique.

Shoulder blade Dornheim Anatomy
Scientific Basis Occlusion Occipital Bone Parietal Bones Scapula Scapula, or shoulder blade is fixated to the axial skeleton solely via clavicle. Motions of the shoulder blade, to a great extent, facilitate the movements of the upper arm. Scapula in situ. Posterior oblique view.

Two views of the Scapula Human anatomy and physiology, Medical knowledge, Yoga anatomy
Margo medialis scapulae Margo medialis scapulae definition. To be filled in. Terms Medial part of scapula Margo medialis (Scapula) Vertebral border of scapula Medial border of scapula Binnenste rand van het schouderblad Margo medialis scapulae introductory description. To be filled in. Margo medialis scapulae Documents, webpages Images Videos

Question Wat is de scapula? Memory
Margo medialis scapulae Description The medial border (vertebral border or vertebral margin) of scapula is the thin, medially located edge of the bone. It extends from the superior angle of the scapula to its inferior angle and is longest of three borders of the scapula, the other two being the lateral and superior borders.

Musculus serratus anterior Muscle anatomy, Body anatomy, Human muscle anatomy
Margo medialis scapulae. Margo lateralis scapulae. Angulus superior scapulae. Angulus inferior scapulae. Fossa infraspinata. Fossa supraspinata. Processus coracoideus. Uploaded by: rva Netherlands, Leiden - Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden University. Creator(s)/credit: Dr Eric Bauer, Biology professor.

MM. RHOMBOIDEI MAJOR ET MINOR processus spinosus C6C7 (minor), T1T4 (major) >>> margo
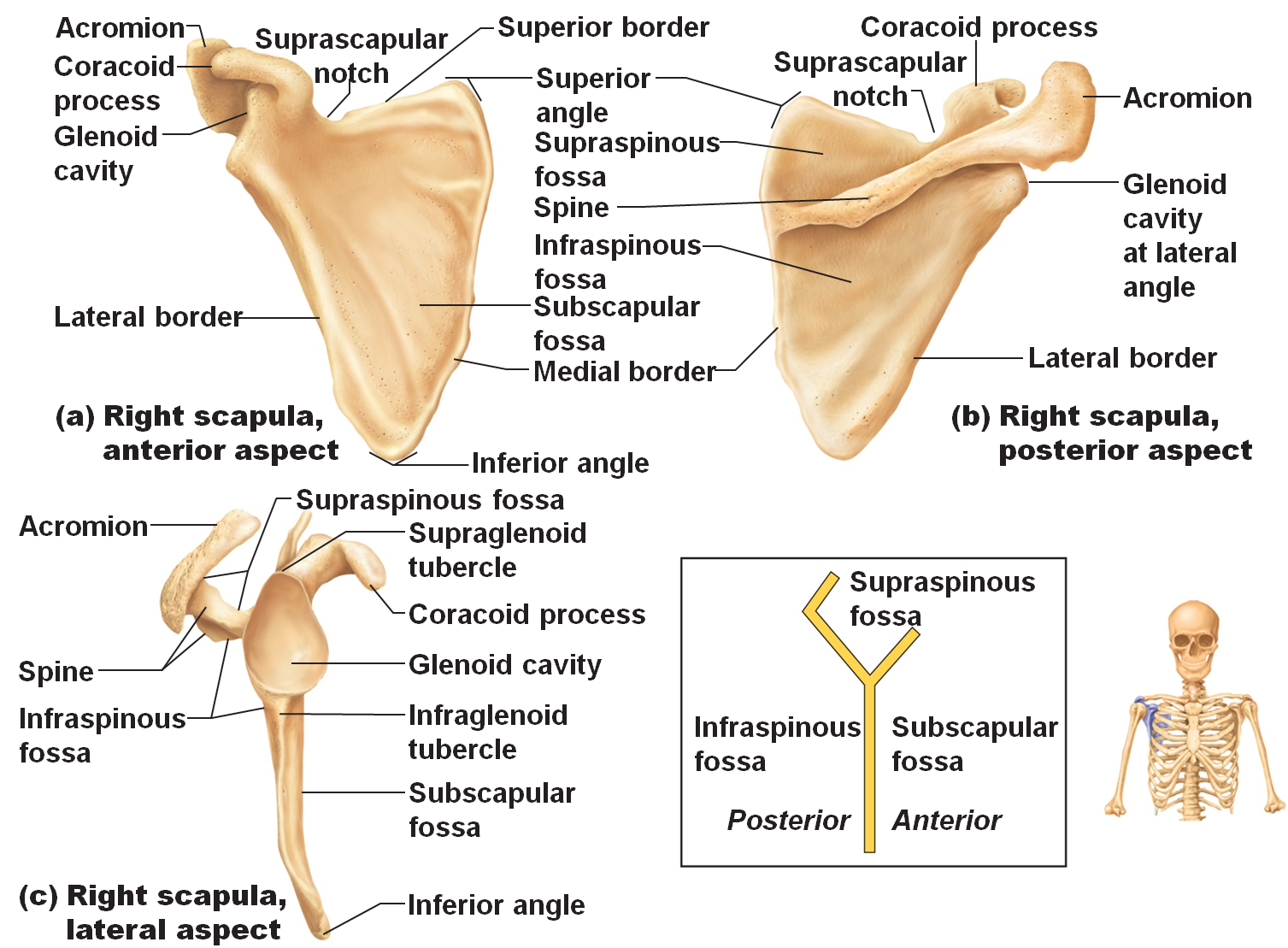
Like any triangle, the scapula consists of three borders: superior, lateral and medial. The superior border is the shortest and thinnest border of the three. The medial border is a thin border and runs parallel to the vertebral column and is therefore often called the vertebral border. The lateral border is often called the axillary border as it runs superolaterally towards the apex of the axilla.

Schulterblatt Dornheim Anatomy
See: medial border of forearm, medial border of foot, medial border of humerus, medial border of kidney, medial border of scapula, medial border of suprarenal gland, medial border of tibia. Synonym (s): margo medialis [TA], medial margin Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary © Farlex 2012 Want to thank TFD for its existence?
A csontvázrendszer
Definition The medial border (vertebral border) is the longest of the three, and extends from the medial to the inferior angle. It is arched, intermediate in thickness between the superior and the axillary borders, and the portion of it above the spine forms an obtuse angle with the part below.
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/medial-border-of-the-scapula/c4vaDMiU0ybz0HPi6DI2mA_medial-border-of-the-scapulaq.png)
Levator scapulae Origin, insertion, innervation, action Kenhub
Medial border (margo medialis) Lateral border (margo lateralis) Superior border (margo superior) Suprascapular notch (incisura scapulae) The scapula has three angles: The superior angle (angulus superior) Superior angle (angulus superior) The inferior angle (angulus inferior) Inferior angle (angulus inferior)

scapula The shoulder blade is the bone that connects the h… Flickr
3.3 Margo medialis (vertebralis) 4 Winkel 4.1 Angulus superior 4.2 Angulus inferior 4.3 Angulus lateralis 5 Prominente Strukturen 5.1 Spina scapulae 5.2 Processus coracoideus 5.3 Acromion 5.4 Cavitas glenoidalis 6 Entwicklung 7 Funktion 8 Klinik 9 Podcast 10 Bildquelle Definition Die Scapula bildet den hinteren Teil des knöchernen Schultergürtels.

Scapulalopatica
Margo medialis scapulae är det latinska namnet på skulderbladets mediala kant. Synonymer margo vertebralis scapulae, "skulderbladets kant som vetter mot ryggraden. Margo medialis är skulderbladets längsta kant. Den sträcker sig från benets övre vinkel ( angulus superior) till dess nedre ( angulus inferior ).

Schulterblatt Dornheim Anatomy
The scapula. Incisura scapulae Incisura scapulae Tuberculum infraglenoidale Tuberculum infraglenoidale Tuberculum supraglenoidale Tuberculum supraglenoidale Acromion Acromion Fossa subscapularis Fossa subscapularis Facies costalis; facies anterior Facies costalis; facies anterior Collum scapulae Collum scapulae Tuberculum infraglenoidale.

Презентация на тему "Кости верхней конечности. ООМК. г.Оренбкрг. Коломак В.А г". Скачать
The scapula is a thick, flat bone lying on the thoracic wall that provides an attachment for three groups of muscles: intrinsic, extrinsic, and stabilizing and rotating muscles. The intrinsic muscles of the scapula include the muscles of the rotator cuff —the subscapularis, teres minor, supraspinatus, and infraspinatus. [3]

Level 8 Skelett der oberen Extremität I Propädeutik Makroanatomie… Memrise
The scapula is only connected to other bones via the clavicle. Latin labels. Image retrieved from Anatomy Standard, page Scapula. Anatomical structures in item: Scapula. Facies posterior scapulae. Angulus superior scapulae. Margo superior scapulae. Fossa supraspinata.
medical freak THE SKELETON OF THE UPPER LIMB
The approach to remove subscapular tumours requires elevation of the scapula usually by detaching the rhomboid muscles from the margo medialis of the scapula [1] - [9]. As these muscles directly insert into the periosteum without tendons, stable refixation is rendered difficult, because sutures easily pull out of the muscle tissue.